Guide to wealth creation: When to start investing ?
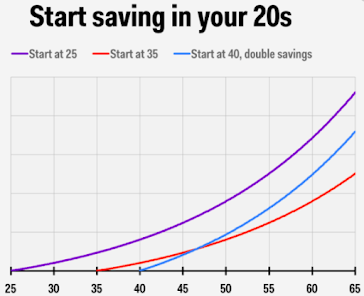
Investing when you are young is one of the best ways to see solid returns on your money. Thanks to compounded earnings, which means your investment returns start earning their own return. A typical example of compounding can be seen in this example, if a person had started investing at the age of 25 and he/she was investing ₹ 5,000 per month and earned @10% p.a. on his investments. In all, he/she would invest ₹ 21 lacs and accumulate a sum of ₹ 1.70 crores at 60 years of age.
Before you begin
But before you start investing you need to save some money. Whenever you pop this question of "When should I start investing", a popular opinion is to start it as soon you get your first salary. But you should check where you are from a financial standpoint. It does not make sense to invest money if you have a significant amount of debt and no emergency fund.Also, paying off your debt (especially credit card debt) and saving for emergencies, you will free up more of your cash for investing.
Avenues to invest:
There are multiple investment options to choose from in India:
- Fixed Deposits - are regarded as one of the most popular investments in India. They provide a fixed rate of return for a specific period and considered as a low-risk option.
- Mutual Funds - When you invest in mutual funds, you invest in a vehicle that pools money from different investors and channels this into diversified assets.
- Recurring Deposits - Like FDs, Recurring Deposits (RDs) allow an investor to save a specific sum in periodic instalments, but they do not have a lock-in period.
-
Public Provident Fund - The PPF is a long-term savings scheme backed by the Government of
India with a lock-in period of 15 years.
- Employee Provident Fund - The EPF is a retirement savings scheme specifically for salaried employees. Monthly contributions are made from an employee’s salary, while the employer contributes an equivalent amount to the corpus.
- National Pension Scheme - NPS is a retirement pension scheme introduced by the Government of India. Through regular investments, you can build a corpus that can provide you with a regular pension after retirement. Investors can also withdraw from the fund partially after retirement.
-
Stocks - Purchasing shares in a company and giving the investor ownership
stake. It can be profitable when the company grows in future, however
it can be risky.
Where to invest money
There is no one-size-fits-all investment plan. For each investor, the ideal portfolio will depend on several variable factors like age, investment horizon, goals, and risk capacity.
When you are young, your risk-taking capacity could be higher. Therefore, investing in equities and mutual funds can be a good option. Older investors can afford fewer risks and hence, one could invest in safer vehicles like fixed deposits.
Certain other factors like one’s disposable income, debt profile, and dependent responsibilities can also impact the investor’s investment decisions.